
Predictive Maintenance: Smart failure prevention for forward-looking maintenance
8. September 2025
Imagine being able to avoid unplanned failures and costly maintenance before they even occur. Predictive Maintenance makes this possible and revolutionises the way companies optimise their operations and conserve resources. In a world where production downtimes cause high costs and efficiency becomes a competitive advantage, Predictive MaintenancePredictive maintenance using data analysis and AI to forecast machine failures before they occur. offers invaluable added value.
Would you like to know how to successfully implement Predictive Maintenance, what economic benefits it offers and which challenges must be overcome? This article provides the answers and shows how Predictive Maintenance can transform your operations, and how IoT, Machine Learning and Big Data can help you prevent equipment failures and reduce costs.

1. Introduction to Predictive Maintenance
Predictive Maintenance (PdM) is a strategy based on monitoring the condition of machines and equipment in order to carry out maintenance work only when it is actually required. This forward-looking approach uses advanced technologies such as IoT sensors, Machine LearningMachine Learning – algorithms for autonomous pattern recognition in production data for automatic process optimization without manual programming. and Big DataHuge amounts of data that are too large and complex for conventional data processing software. Analytics to predict the optimal time for maintenance. Continuous data such as vibration, temperature and pressure values are collected and analysed to identify patterns and anomalies that indicate impending failures.
Difference between Predictive and Preventive Maintenance
While Predictive Maintenance is based on forecasting failures, Preventive Maintenance relies on regular, time-based maintenance. Preventive Maintenance is carried out at fixed intervals or usage cycles, regardless of the actual condition of the machine, which can lead to unnecessary maintenance actions and associated costs. In contrast, Predictive Maintenance intervenes in a targeted and efficient manner as soon as an actual need arises, thereby reducing maintenance costs and increasing machine availability.
Set new standards in maintenance!
Maximise efficiency and precision in your production – for sustainable competitiveness and future security. Discover our IIoT monitoring platform Clouver now!
2. Technological Foundations and Innovations
IoT sensor technology and developments
IoT sensors continuously collect data on the condition of machines and systems. These sensors can measure various physical parameters such as vibration, temperature and pressure. Real-time data enables precise monitoring and early detection of potential disruptions. The development of ever smaller and more powerful sensors, as well as their integration into existing systems, has significantly improved the spread and efficiency of Predictive Maintenance.
Machine Learning algorithms for smart maintenance
Machine Learning algorithms analyse the collected data and identify patterns that indicate impending failures. These algorithms continuously learn from historical data and current measurements to enable increasingly accurate predictions. By applying techniques such as anomaly detection and predictive modelling, maintenance teams can take early action to prevent serious problems.
Edge ComputingData processing directly on-site at machines and sensors, without detour via central servers or cloud. in maintenance
Edge Computing enables data processing directly at the source, i.e., near the machines. This reduces latency and enables faster responses to potential problems. Decentralised data processing allows large data volumes to be handled efficiently without constantly transferring them to central data centres. This is particularly useful in environments with limited connectivity or high latency requirements.
Impact of 5G on Predictive Maintenance
The introduction of 5G technology enables faster and more reliable data transmission. With higher bandwidths and lower latencies, 5G significantly improves communication between IoT sensors and central data platforms. This leads to more efficient data processing and enables real-time analyses that further enhance the efficiency of Predictive Maintenance systems. 5G also supports the integration and use of Augmented Reality and other technological advances in maintenance processes.
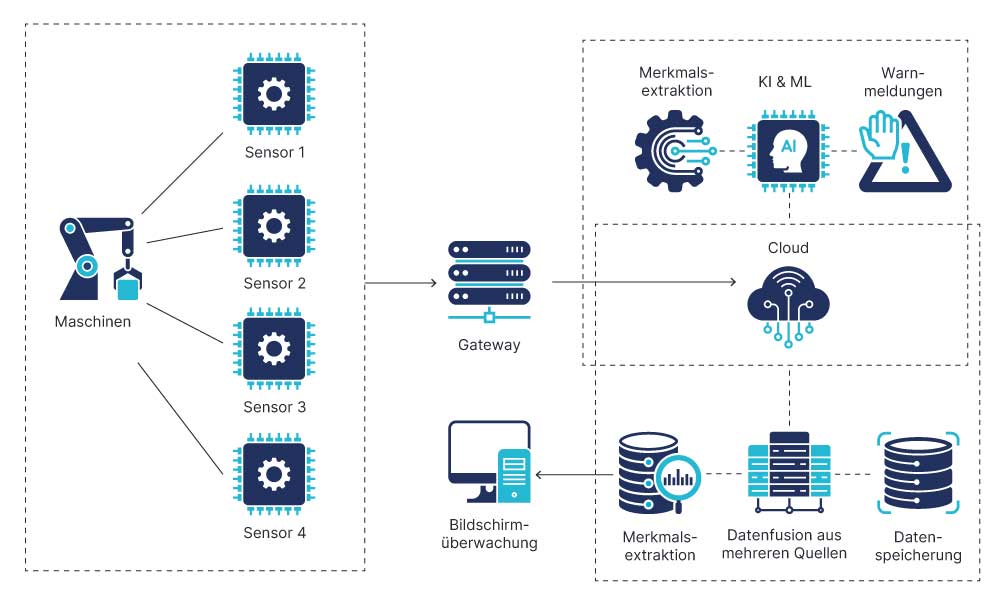
3. Implementation and Best Practices
Successful implementation of Predictive Maintenance requires a clear strategy that equally considers technical, organisational and human factors.
- Needs Assessment: Analyse which machines and processes have the greatest impact on productivity and costs. Consider failure rates, maintenance intervals and existing data sources to realistically assess the potential for Predictive Maintenance.
- Technology Selection: Choose appropriate IoT sensors, data platforms and analysis tools that are compatible with your existing IT and production environment. Scalability and data security should be key decision criteria.
- Pilot Project: Start with a clearly defined use case to test effectiveness and gain initial experience. A successful pilot provides valuable insights into data quality, process integration and training needs.
- Scaling and Change Management: Gradually transfer proven processes into regular operation. Accompany the introduction with targeted training to promote acceptance and competence within the team. Good change management is crucial to avoid resistance and fully realise the benefits of the new technology.
A well-founded business case supports the argument for investment. In addition to direct cost savings through reduced downtimes, long-term effects – such as higher equipment availability and extended lifespan – should also be considered. This allows the return on investment (ROI) to be presented transparently and comprehensibly.
4. The Role of Big Data and Analytics
Data collection and analysis
Continuously collect data from your machines and systems and use advanced analysis tools to interpret this data and gain valuable insights. Accurate data collection and analysis are crucial for making precise predictions and informed decisions. Use both historical and real-time data to gain comprehensive insights into the condition and performance of your machines.
Integration of data sources
Ensure that all relevant data sources are consolidated on a central platform. This enables comprehensive analysis and better predictions. Integrate data from various systems such as ERPEnterprise Resource Planning – software for integrated management of all business processes and resources., CMMS and IoT platforms to obtain a complete picture and support data-driven decision-making.
Please also read our article on this topic: What is Industrial Internet of Things (IIoTIIoT is the internet-based networking of industrial machines, systems, and devices for data collection and process optimization.)?
Using Predictive Analytics for forward-looking maintenance
Use Predictive Analytics to accurately forecast future maintenance needs, thereby maximising the efficiency and availability of your assets. Predictive Analytics combines statistical models, machine learning and data analysis techniques to identify patterns and trends that indicate upcoming maintenance requirements. This enables proactive actions and improves the planning and execution of system maintenance.
5. Industry-specific Applications
Manufacturing 4.0
Predictive Maintenance is a central component of Industry 4.0 and helps manufacturing companies minimise downtimes and increase productivity. Through the integration of IoT sensors and data analyses, manufacturers can continuously monitor the condition of their machines and plan maintenance measures as needed. This leads to higher efficiency and better resource utilisation.
Energy sector and utilities
Energy providers can use Predictive Maintenance to increase the reliability of their networks and reduce repair costs. Continuous monitoring of transformers, generators and other critical components enables early intervention and prevents costly failures. This contributes to the stability and efficiency of energy supply.
Healthcare equipment
Hospitals and other healthcare facilities use Predictive Maintenance to ensure the availability and safety of medical equipment. By monitoring diagnostic devices, ventilators and other vital equipment, potential problems can be detected and corrected early, increasing patient safety and reducing operating costs.
Smart buildings
In intelligent buildings, Predictive Maintenance ensures the smooth operation of heating, ventilation and air-conditioning systems. Sensors continuously monitor the condition of HVAC systems and report anomalies before they lead to major problems. This improves comfort and energy efficiency while reducing service costs.
Process industry
In the process industry, Predictive Maintenance helps maximise the availability and efficiency of complex systems. By monitoring pumps, valves and other critical components, companies can ensure their production systems function optimally and minimise unplanned downtimes.
6. Data Security and Compliance
- Cybersecurity in Predictive Maintenance systems: Implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect your data and systems from unauthorised access and attacks. This includes data encryption, the use of firewalls and intrusion detection systems, as well as regular security checks and updates. Ensure that all systems and networks meet the highest security standards.
- Data protection aspects: Ensure that your Predictive Maintenance solutions comply with all relevant data protection regulations. This includes compliance with regulations such as the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and other regional data protection laws. Implement data protection policies and procedures to guarantee the confidentiality and integrity of the collected data.
- Industry standards and certifications: Adhere to industry standards and certifications to ensure the quality and security of your Predictive Maintenance systems. These include standards such as ISO 27001 for information security management and ISO 55001 for asset management. Compliance with these standards demonstrates your company’s commitment to best practices and continuous optimisation.
- Cloud vs. on-premise solutions: Weigh the advantages and disadvantages of cloud-based and on-premise solutions to choose the best option for your company. Cloud-based solutions offer scalability, flexibility and lower initial costs, while on-premise solutions provide greater control over data and systems. Consider your specific requirements and resources to find the optimal solution.
7. Economic Aspects
Cost-saving potential
Predictive Maintenance helps reduce maintenance costs and avoid expensive downtimes. By detecting and fixing problems early, companies can minimise unplanned stoppages and improve the efficiency of maintenance intervals. This leads to significant cost savings and higher profitability.
Increased availability
By detecting problems early, the availability of your machines and systems is maximised. Predictive Maintenance helps increase uptime and maximise production capacity by ensuring that equipment remains in optimal condition.
Optimisation of human resources
Optimise the use of your maintenance teams and improve the planning of maintenance tasks. Predictive Maintenance enables more efficient use of personnel resources by scheduling maintenance work based on actual needs rather than rigid timetables. This results in better workload distribution and higher employee satisfaction.
Insurance aspects
Predictive Maintenance can lead to lower insurance premiums, as the risk of failures and damages is reduced. Insurance companies recognise the benefits of Predictive Maintenance and often offer lower rates to companies that implement these technologies.
Total Cost of Ownership
Reduce the total cost of ownership (TCO) of your machines and systems through more efficient maintenance and longer lifespan. Predictive Maintenance helps lower the TCO by minimising unplanned downtimes, extending machine life and improving maintenance efficiency.

Read also our: Clouver Brochure – your IIoT solution for greater transparency and efficiency in production
8. Integration and Interfaces
Predictive Maintenance unleashes its full potential only through seamless integration into existing systems.
ERP systems link maintenance information with production and operational data, creating a central foundation for planning, analysis and control.
CMMS systems (Computerised Maintenance Management Systems) allow maintenance orders to be automatically generated, documented and tracked – for maximum transparency and efficiency.
IoT platforms continuously collect sensor data and, in combination with cloud services, enable scalable data storage and real-time analysis of large data volumes.
Mobile solutions ensure that technicians always have access to up-to-date information and can carry out maintenance tasks efficiently on-site.
Thoughtful system integration thus ensures smooth information flow – from the machine to management level – and forms the basis for a connected, data-driven maintenance strategy.
9. Future Trends and Developments
- AI-Supported Predictive Maintenance: Artificial Intelligence (AI) will further improve the accuracy and efficiency of Predictive Maintenance. Through the use of advanced algorithms and machine learning, AIArtificial Intelligence – computer systems that can simulate human-like thinking processes and decisions. systems can identify complex patterns and relationships in large data sets that are difficult for human analysts to detect. This enables more precise predictions and more proactive maintenance strategies.
- Autonomous Maintenance: Autonomous maintenance systems could perform maintenance tasks in the future without human intervention. Through the use of robotics and AI, such systems can carry out inspections, diagnoses and repairs independently, further increasing the efficiency and accuracy of maintenance processes.
- Sustainable Maintenance: Sustainable maintenance practices aim to minimise the ecological footprint of maintenance work. By using Predictive Maintenance, companies can reduce energy consumption and waste generation by performing maintenance only when it is truly necessary. This helps protect the environment and achieve sustainability goals.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Predictive Maintenance is more than just a trend – it marks a turning point in maintenance technology. By using IoT sensors, Machine Learning and Big Data Analytics, it enables precise forecasts of maintenance needs and reduces downtimes and costs. Companies thus increase their efficiency, extend the lifespan of their machines and conserve resources.
The technology is highly versatile from manufacturing and the energy sector to smart buildings and healthcare. Predictive Maintenance not only reduces operating costs but also promotes sustainability by avoiding unnecessary repairs and energy waste.



