
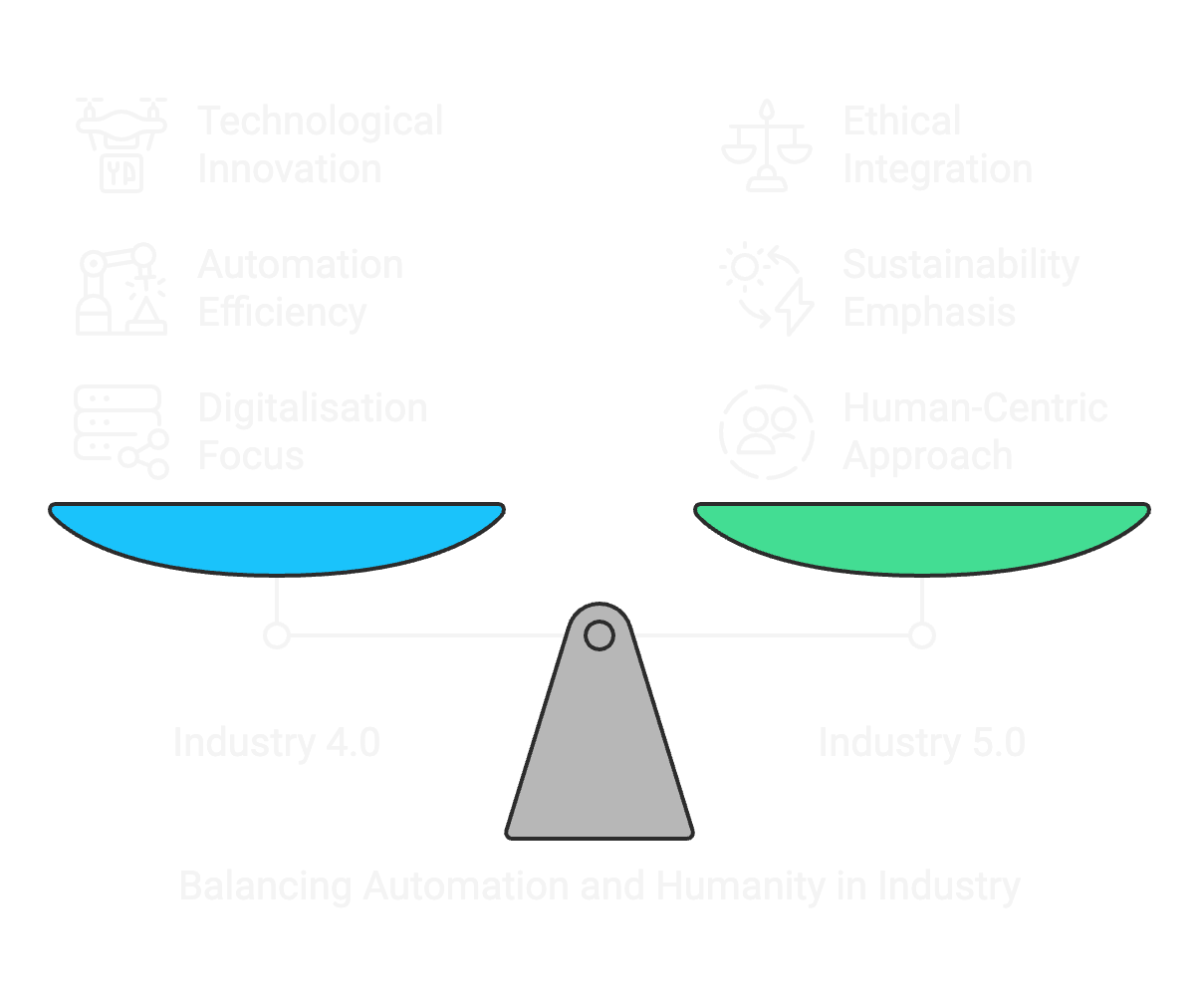
Industry 5.0 describes the next stage of the industrial revolution, which significantly differs from Industry 4.0 by placing humans back at the centre. While Industry 4.0 focused heavily on automation and networking, Industry 5.0 aims to optimise the collaboration between humans and machines to enable personalised, efficient, and sustainable production. The central idea is to use technology not only as a tool for increasing efficiency but also for improving working conditions and promoting human creativity and innovative power.
Your Partner for Innovative Automation Solutions!
ProCom offers the perfect combination of intelligent software, premium hardware, and comprehensive support. Whether knife, laser, or waterjet cutting – we'll develop the ideal solution for your production needs. Arrange your consultation today and get started!
Technological Pillars of Industry 5.0
Quantum Computing and its Role
Quantum computing represents a revolutionary technology that enables extremely high computing power, which is essential for processing complex industrial processes. Unlike classical computers based on binary systems, quantum computers use quantum bits or qubits that can assume multiple states simultaneously. This leads to an exponential increase in computing power and enables the solution of problems that are inaccessible to classical computers. Companies should begin to learn about possible applications in their industry and conduct pilot projects to test the potential of this technology.
Advanced Robotics and Cobots
Advanced Robotics and collaborative robots (cobots) play a crucial role in Industry 5.0 by supporting human work in production. Cobots are designed to work safely and efficiently with humans by taking over repetitive, dangerous, or physically demanding tasks. This enables human workers to focus on more complex and creative tasks. Companies should analyse their workflows to identify areas that can be supported by cobots and train their employees in working with these technologies.
Digital Twins and Simulation
Digital twins are virtual models of physical objects or systems that enable the simulation and optimisation of production facilities. They provide a platform for continuous monitoring and analysis of production processes by collecting and evaluating real-time data. By creating digital models, companies can improve the performance and efficiency of their facilities, identify potential problems early, and minimise costly downtime. This leads to overall more efficient and flexible production.
Edge Computing in Production
Edge computing enables real-time data processing directly at the production line, eliminating the need to first transfer data to central data centres. This reduces latency times and enables faster reactions to production events. Edge computing devices can be implemented at critical points in the production line to enable immediate process improvements and increase overall productivity. Companies should install these devices at strategic points and use the data gained for immediate process improvement.
Blockchain Integration
Blockchain technology offers significant advantages regarding the security and transparency of supply chains. By implementing blockchain solutions, companies can ensure that all transactions and data are tamper-proof and transparent. This increases trust in the supply chain and enables seamless tracking of products from origin to end consumer. Companies should identify touchpoints in their supply chain where blockchain technology can offer benefits and implement appropriate solutions.
Automation and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Automation remains a central component of Industry 5.0, with Artificial Intelligence (AI) playing a crucial role. AI technologies enable the optimisation of production processes through machine learning and data analysis. They improve decision-making by processing large amounts of data in real-time and recognising patterns that would be barely visible to human analysts. Furthermore, AI supports predictive maintenance by predicting machine failures and recommending preventive measures. By using AI, companies can increase efficiency and minimise downtime, leading to improved productivity and cost efficiency.
Sensors, Connectivity and Smart Manufacturing
Advanced sensors and connectivity are essential for smart manufacturing, which aims to digitise and network the entire value chain. Through the use of IoT sensors, companies can collect real-time data about all aspects of their production, from raw material delivery to final product packaging. This data enables improved collaboration between customers and suppliers, optimised inventory management, and faster responsiveness to market changes. The integration of the entire value chain leads to more seamless and efficient production, improving both quality and production speed.
Human-Machine Interaction
The interaction between humans and machines is being revolutionised through cognitive ergonomics, intuitive interfaces, and Augmented Reality (AR). Cognitive ergonomics aims to design workplaces that correspond to the cognitive and physical abilities of employees, thereby improving efficiency and well-being. Intuitive interfaces make it easier to operate complex machines and systems, whilst AR technologies provide employees with visual support and real-time instructions. These technologies contribute to improving working conditions, increasing safety, and boosting productivity. Companies should ergonomically adapt their workplaces and use AR glasses to support their employees to create optimal working conditions.
Sustainability and Resource Efficiency
Sustainability is a central theme in Industry 5.0. The development of strategies for circular economy and material optimisation is crucial to efficiently use resources and minimise waste. Energy management systems can be implemented to monitor and control energy consumption, leading to a reduction in CO2 emissions. Green manufacturing practices promote the use of environmentally friendly materials and production methods. Companies should develop sustainable strategies to minimise their ecological footprints whilst increasing their competitiveness.
Socioeconomic Aspects
Industry 5.0 is changing the job market and creating new professional profiles that require specialised skills and continuous training. Companies must prepare their workforce for the future by developing training programmes and promoting continuous education. Work-life balance and ethical considerations should also be taken into account to create a positive working environment. Promoting diversity and inclusion can increase a company's innovative power and help ensure that all employees can reach their full potential.
Implementation and Change Management
A successful transformation to Industry 5.0 requires clear transformation strategies and thorough cost analysis. Pilot projects can help test the feasibility and benefits of new technologies. Employee qualification is crucial to ensure that the workforce is able to effectively use new technologies. The use of best practices and case studies can facilitate the transition by providing valuable insights and practical advice. Companies should pursue a structured approach that considers all aspects of implementation and change management.
Regulatory Framework
Ensure that your implementations comply with international standards and regulations. This includes compliance with safety and data protection regulations as well as consideration of industry-specific requirements. Research relevant standards and integrate these into your planning processes to minimise legal risks and ensure compliance.
Future Perspectives
Stay up to date on current research trends and innovations in Industry 5.0. Attend conferences, network with research institutions, and subscribe to scientific journals to stay informed. Continuous observation and adaptation to new developments is crucial to remain competitive and benefit from the latest technologies and best practices.
Concrete Application Examples
Learn from successful implementations in your industry. Analyse case studies and best practices to transfer and adapt the success criteria to your company. Concrete examples provide valuable insights into the challenges and solutions that other companies have experienced when introducing Industry 5.0 technologies.
Supplementary Statistics and Facts
Use current market data on Industry 5.0 adoption, investment figures, and productivity metrics to make informed decisions. This data can help you better understand the potential benefits and risks of implementing new technologies and plan your investments accordingly.
Practical Additions
Use checklists, assessment matrices, and KPI frameworks to plan and monitor the implementation of Industry 5.0 technologies. These tools can help you measure progress, define success criteria, and ensure that your implementations deliver the desired benefits.
Conclusion
Industry 5.0 marks a significant turning point in the development of industrial production. While Industry 4.0 focused on automation and networking, Industry 5.0 brings humans back to the centre. The collaboration between humans and machines is further optimised through advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, robotics, and the Internet of Things (IoT). This leads to more personalised, efficient, and sustainable production. Industry 5.0 promotes not only productivity but also creativity and innovative power of employees.
Are you curious and would like to learn more about the fascinating possibilities of Industry 5.0? Then we invite you to read our further content and delve deeper into the topics. Visit our articles about the latest technologies and trends in Industry 5.0.

Sergej Gigel
Senior Sales Manager
Have questions about the topic or want to learn more about our solutions?
Contact us and discover how our products can future-proof your machines. Let’s work together to find out how we can help take your production to the next level!
- +49 241 93681-500
- contact@procom-automation.de

