

In today's digital era, efficient and reliable management of machines and equipment is essential for businesses. This is where the concept of predictive maintenance comes into play. But what exactly lies behind the term predictive maintenance, and why is it so relevant for modern industrial companies?
Predictive maintenance enables the early detection and targeted prevention of potential disruptions through real-time data analysis. This allows companies to minimise expensive downtime, extend the lifespan of their equipment, and increase economic efficiency. But how does this technology work specifically, and what prerequisites must be met to implement it successfully?
In this article, we answer all your questions about predictive maintenance, from the technological foundations through implementation strategies to industry-specific applications and future developments. We not only show you the numerous advantages but also provide practical tips and best practices to make getting started easier. Let yourself be inspired and discover how predictive maintenance can revolutionise your company!
Introduction and Fundamentals
Significance and Definition of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is a smart way to keep machines running efficiently by constantly monitoring their condition. that continuously monitors the condition of machines and equipment. By using real-time data and advanced technology, it aims to plan maintenance measures based on needs before machine failure occurs. Instead of waiting for failures like in reactive maintenance, and preventive maintenance, which follows fixed time intervals, predictive maintenance is based on the actual condition and usage of the devices.
This method uses extensive data to make precise predictions about maintenance requirements, leading to more efficient resource utilisation and higher operational reliability. Especially in industries where machinery is expensive and complex, predictive maintenance offers significant advantages by avoiding unforeseen downtime and extending equipment lifespan.
Differences from Other Maintenance Strategies
Compared to traditional maintenance strategies, predictive maintenance offers clear advantages:
Reactive Maintenance: Maintenance occurs only after a fault or failure occurs. This method can lead to high downtime costs and unexpected production interruptions.
Preventive Maintenance: Regular maintenance work is carried out at fixed time intervals, regardless of the machine's condition. This can lead to unnecessary maintenance work and increased costs when no problems are present.
Predictive Maintenance: Maintenance measures are planned based on real-time data and condition analyses. This enables precise and needs-based maintenance that reduces costs and increases equipment efficiency.
Through the use of predictive maintenance, maintenance work is planned more efficiently, leading to minimisation of unplanned downtime and optimal resource utilisation. Unlike preventive maintenance, it is more flexible and accurate as it is based on actual usage and condition of the machines.
Objective and Benefits of Predictive Maintenance
The main objective of predictive maintenance is to maximise the efficiency and reliability of machines and equipment. Through early detection of potential problems, maintenance measures can be carried out in a targeted and timely manner before serious damage occurs. The benefits include:
Reduction of maintenance costs: Need-based maintenance avoids unnecessary work and efficiently utilises resources. Extension of equipment lifespan: Regular and targeted maintenance prevents premature wear and increases machine longevity. Increase in productivity: Less downtime means continuously high production capacity. Enhancement of safety: Early problem detection contributes to employee and production facility safety. Optimisation of resource planning: Maintenance work can be better planned and prioritised, improving overall operations management.
These advantages make predictive maintenance an indispensable strategy for modern industrial companies seeking to increase their competitiveness and reduce operating costs.
Technological Foundations
Sensor Technologies and Their Application
One of the essential components of predictive maintenance is the sensors used to record various operating parameters. These sensors continuously measure data such as vibrations, temperatures, pressure, humidity, and electrical currents. The precise measurements enable accurate monitoring of equipment condition.
Advanced sensor technologies, such as vibration sensors, temperature sensors, and acoustic sensors, provide the necessary real-time data. Modern sensors are often equipped with wireless communication capabilities, allowing them to be seamlessly integrated into existing IT infrastructures. For example, Procom ensures reliable data collection for predictive maintenance through high-quality sensors in their CNC machines.
Data Analysis Tools and Software Solutions
The collected data must be efficiently processed and analysed to gain useful insights. This is where specialised data analysis tools and software solutions come into play. These programmes enable the processing of large amounts of data and the identification of patterns that indicate potential problems.
Clouver, a leading software in production monitoring, offers powerful analysis functions specifically tailored to predictive maintenance requirements. Such tools use statistical analyses and machine learning to detect deviations in equipment operation and make predictions about maintenance needs.
Clouver makes it easy to collect, visualise, and analyse data from every machine in your production chain, from raw material to finished product!
Boost Your Productivity with Clouver!
With our powerful IIoT platform, you'll have complete control over your production processes at all times. Reduce downtime, optimise resource usage, and stay ahead of your competition. Schedule your personal consultation now and discover how Clouver can support you!
Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine Learning (ML) algorithms are a central component of predictive maintenance. They process historical and real-time data to recognise patterns and connections that might escape human analysts. These algorithms can continuously learn from new data and improve their prediction accuracy.
Through the use of ML algorithms, companies can make more precise predictions about the condition of their machines and thereby plan more targeted maintenance measures. This leads to higher efficiency and reliability of production processes.
IoT Infrastructure and Connectivity
A robust IoT (Internet of Things) infrastructure is essential for the successful implementation of predictive maintenance. It ensures that all sensors and devices reliably communicate with each other and that the collected data is transmitted in real-time. Stable connectivity enables data to be seamlessly sent to central databases or cloud services such as Clouver's solutions, where it can be analysed and evaluated.
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
There are two main approaches to data processing in predictive maintenance:
Edge Computing: Here, data is processed directly at the source, near the location of the machines. This reduces latency times and enables faster response times in anomaly detection. It also relieves the central IT infrastructure as only relevant data is forwarded.
Cloud Computing: Cloud-based solutions provide a central platform for data storage and processing. They allow scalable analysis of large amounts of data and the use of advanced analysis tools. However, higher security and data protection requirements may exist.
The choice between Edge and Cloud Computing depends on the specific requirements of the company. Often, both approaches are combined to utilise the advantages of both technologies.
Functionality of Predictive Maintenance
Data Collection through Sensors and Monitoring
The foundation of predictive maintenance is continuous data collection through various sensors. These sensors monitor essential operating parameters such as temperature, vibration, pressure, and humidity. The collected data is recorded in real-time and forwarded to central databases. With high-quality CNC machines from Procom and the use of Clouver software, it is ensured that the data is precise and reliable.
Real-time Analysis and In-memory Databases
Real-time analysis of collected data is crucial for early detection of anomalies. In-memory databases enable fast processing and evaluation of large amounts of data directly in working memory. This enables immediate response to detected problems and improves decision-making.
Clouver offers powerful tools for real-time analysis that enable companies to quickly react to changes in equipment condition and take necessary measures.
Condition Assessment
Condition assessment can occur in two forms: periodic and continuous.
Periodic Condition Assessment: Here, data is evaluated at regular intervals to check the condition of machines. This is helpful for equipment that is rarely used or whose condition changes slowly.
Continuous Condition Assessment: This method is based on ongoing monitoring and analysis of data. It enables immediate detection of problems and proactive maintenance, thereby maximising equipment availability.
Various Test Methods
Predictive maintenance uses various test methods to assess machine condition. These include:
Infrared Thermography: Measures temperature distribution of machine components to detect overheating or other thermal anomalies. Acoustic Analyses: Identifies unusual noises that could indicate mechanical problems. Vibration Analyses: Captures and analyses vibration patterns to detect wear or imbalances in rotating parts.
Each of these methods offers specific advantages and can be used depending on the application area and machine type to obtain a comprehensive picture of equipment condition.
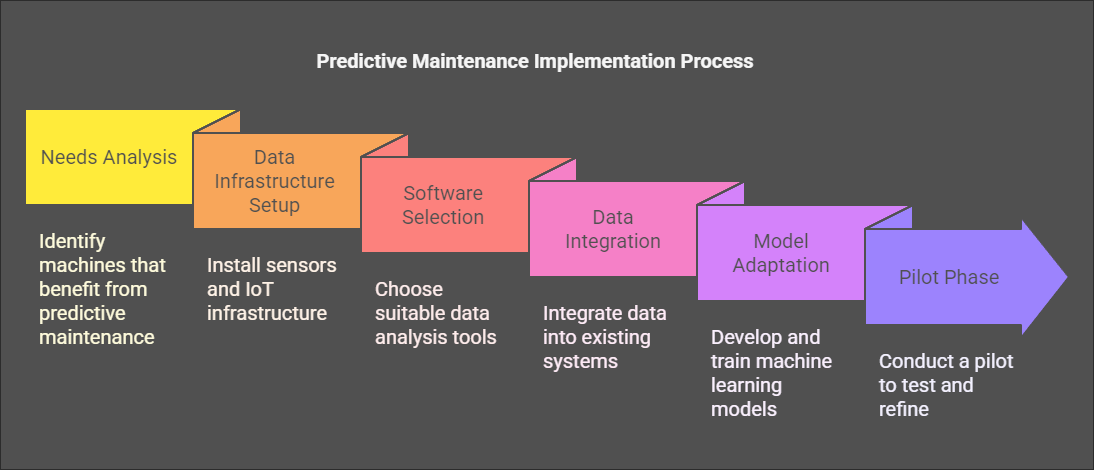
Implementation and Integration
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide
The implementation of predictive maintenance requires a systematic approach comprising several steps:
- Needs Analysis: Identify the machines and equipment that would benefit most from predictive maintenance.
- Data Infrastructure Setup: Install necessary sensors and ensure reliable IoT infrastructure to capture and transmit data.
- Software Selection: Choose suitable data analysis tools and software solutions like Clouver that are tailored to your specific requirements.
- Data Integration: Integrate collected data into your existing systems and ensure it is available for analysis.
- Model Adaptation: Develop and train machine learning models tailored to your specific machines and operating conditions.
- Pilot Phase: Conduct a pilot phase to test implementation and refine models.
- Scaling: After successful tests, scale solutions to all relevant machines and equipment in the company.
This structured approach ensures smooth implementation and achievement of desired results.
Cost Analysis and ROI Calculation
A thorough cost analysis is essential to evaluate the economic feasibility of predictive maintenance. Both initial investment costs for sensors, software, and infrastructure, as well as ongoing operating costs should be considered. At the same time, potential savings through reduced downtime, longer equipment lifespan, and optimised maintenance processes must be calculated.
Return on Investment (ROI) calculation is an important step to demonstrate the economic benefit of implementing predictive maintenance. For example, companies can achieve positive ROI within a few years through reduction of unplanned downtime and prevention of expensive repairs.
Change Management in Implementation
The introduction of predictive maintenance requires not only technological adaptations but also organisational changes. Effective change management is crucial to ensure all employees accept and support the new processes. This includes:
Communication: Transparent and regular communication about the benefits and objectives of predictive maintenance. Employee Involvement: Involvement of employees in implementation and training to promote acceptance and engagement. Adaptation of Work Processes: Integration of new maintenance strategies into existing workflows to ensure seamless transition.
Well-planned change management minimises resistance and increases implementation success chances.
Employee Training and Qualification Requirements
Employee training is an essential component of successful predictive maintenance implementation. Employees must possess necessary knowledge and skills to operate new systems and effectively use gained data. This includes:
Technical Training: Imparting knowledge about operation and maintenance of new sensors and software solutions. Data Analysis: Training in handling data analysis tools and interpreting results. Processes and Procedures: Adapting maintenance processes to new strategies and technologies.
Targeted training programmes ensure staff is optimally prepared and can fully exploit predictive maintenance benefits.
Integration into Existing Maintenance Systems
Seamless integration of predictive maintenance into existing maintenance systems is crucial for the efficiency and effectiveness of the overall strategy. This includes:
Compatibility: Ensuring new systems are compatible with existing IT infrastructures and maintenance systems. Data Integration: Incorporating predictive maintenance data into existing databases and management systems to enable holistic overview. Automation: Automating maintenance processes to minimise human intervention and increase efficiency.
Integration into existing systems ensures unified and efficient maintenance strategy that optimises overall operations.
Legal and Security Aspects
Data Protection and GDPR Compliance
When implementing predictive maintenance, all collected data must comply with data protection regulations and GDPR. This ensures user privacy protection and prevents unauthorised access to sensitive data. Companies must establish clear guidelines for data collection, storage, and processing and ensure all data protection requirements are met.
IT Security in Networked Systems
Security of networked systems is a crucial aspect of predictive maintenance. Comprehensive measures must be taken to protect systems from cyber attacks and ensure data integrity. This includes firewalls, encryption technologies, and regular security checks. A robust IT security strategy prevents data loss and unauthorised access to critical information.
Liability Issues in Automated Decisions
Automated decisions in predictive maintenance context can raise legal liability questions. It is important to define clear responsibilities and processes to minimise legal risks. Companies must ensure automated systems are transparent and traceable and that clear liability regulations exist in case of incorrect decisions.
Standardisation and Norms
Compliance with standards and norms ensures predictive maintenance solutions are safe and reliable and meet legal requirements. Standards such as ISO 55000 (Asset Management) and ISO/IEC 27001 (Information Security) provide frameworks that support companies in implementing and operating predictive maintenance.
Future Trends and Developments
Artificial Intelligence and Deep Learning in Maintenance
Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Deep Learning in predictive maintenance will further improve prediction accuracy. These technologies enable deeper analysis of complex data patterns and offer new possibilities for optimising maintenance processes. Through AI use, companies can make even more precise predictions and further increase production facility efficiency.
Digital Twin Technology
Digital Twin technology enables creation of digital twins of physical assets that can be monitored and analysed in real-time. This enables detailed simulation and prediction of equipment condition, further optimising planning and execution of maintenance measures. Digital Twins provide exact replication of physical equipment, enabling more precise condition assessment and maintenance planning.
Augmented Reality in Maintenance
Augmented Reality (AR) can support maintenance technicians in executing complex tasks more efficiently and accurately. Through visual instructions and real-time data overlays, technicians receive valuable information directly on-site, reducing error rates and shortening maintenance times.
Autonomous Maintenance Systems
Autonomous maintenance systems based on Artificial Intelligence could independently perform many maintenance tasks in future. These systems could automatically detect problems, make diagnoses, and even carry out necessary repair measures, further increasing efficiency.
Predictive Quality as Extension
Predictive Quality extends the concept of predictive maintenance to quality assurance. Through early detection of potential quality problems, companies can take proactive measures to ensure product quality and reduce waste. This leads to improved customer satisfaction and reduces costs for rework and quality controls.
Common Challenges
Data quality and availability are crucial for predictive maintenance success. Insufficient data quality can lead to incorrect predictions and inefficient maintenance measures. Companies should ensure they have robust data collection and processing to obtain accurate and reliable insights.
Integration of predictive maintenance solutions into existing systems can pose a challenge. However, seamless integration is essential to maximise maintenance strategy efficiency. Companies should ensure their predictive maintenance systems are compatible with existing IT infrastructures and maintenance systems.
Employee acceptance is an important success factor for predictive maintenance implementation. Resistance can arise from lack of understanding and insufficient training. Through effective change management and comprehensive training programmes, companies can ensure their employees support and effectively use new technologies and processes.
Technical Debt, the technological debt arising from outdated systems and insufficient maintenance, can be a challenge in implementing predictive maintenance. Companies should ensure their existing systems are kept up-to-date and that they invest in new technologies to continuously improve their operational processes.
Scalability of predictive maintenance solutions is crucial to meet growing requirements and increasing complexity of industrial facilities. Companies should ensure their solutions are flexible and adaptable to handle future growth and new requirements.
Stay Ahead with Clouver
Predictive maintenance is transforming industries by preventing failures, reducing costs, and improving overall efficiency. With Clouver, you gain a powerful tool that helps you make data-driven decisions for a smarter production environment.
Want to see it in action? Book a free demo today!

Dimitri Koneger
Sales Manager
Have questions about the topic or want to learn more about our solutions?
Contact us and discover how our products can future-proof your machines. Let’s work together to find out how we can help take your production to the next level!
- +49 241 93681-500
- contact@procom-automation.de


