
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) – Understanding How it Works
2. January 2025
In modern product development, Computer-Aided Design (CAD) is an indispensable tool. It forms the backbone of industrial innovation, combining precision, efficiency, and creative freedom. CAD systems make it possible to create, simulate, and optimise 3D models long before a physical product exists.
Designers and engineers use CAD to create technical drawings and represent complex ideas in a realistic way. This software not only enables precise planning but also improves coordination between development, manufacturing, and quality assurance.
CAD offers companies a wide range of functions, covering everything from the first sketch to production preparation. In combination with Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) and Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE), it forms a digital process chain that saves time, reduces errors, and enables seamless production.
For companies, the benefits of CAD are clear: greater efficiency, lower costs, and shorter development cycles. The result is a structured and transparent product development process that accelerates innovation.
What is Computer-Aided Design?
Definition and Origin
The term CAD refers to the use of software for computer-assisted design of technical products and systems. Its roots go back to the 1960s, when companies first began using computers to support development processes. With the advent of the first personal computers, CAD quickly spread throughout industry and research.
In the past, drawings and models were created manually on drafting boards. CAD revolutionised this process by enabling the creation of technical drawings and digital CAD models that could be easily produced and edited. This digital transformation significantly increased precision and productivity.
From the Drawing Board to 3D Modelling
In the 1980s, engineers initially used CAD for 2D designs. These representations formed the basis for manufacturing documentation. As computing power and new graphic interfaces advanced, CAD evolved into a powerful tool for both parametric and direct modelling.
Today, 3D CAD enables the creation of complex geometries that dynamically respond to changes. Designers can create, modify, and analyse 3D models – always tailored to the specific requirements of a project. CAD is used not only for design purposes but also for the visualisation and simulation of technical processes.
CAD is often referred to as the foundation of digital product development. It facilitates collaboration between teams, departments, and external partners, forming the basis for modern industrial processes that are precise, connected, and efficient.
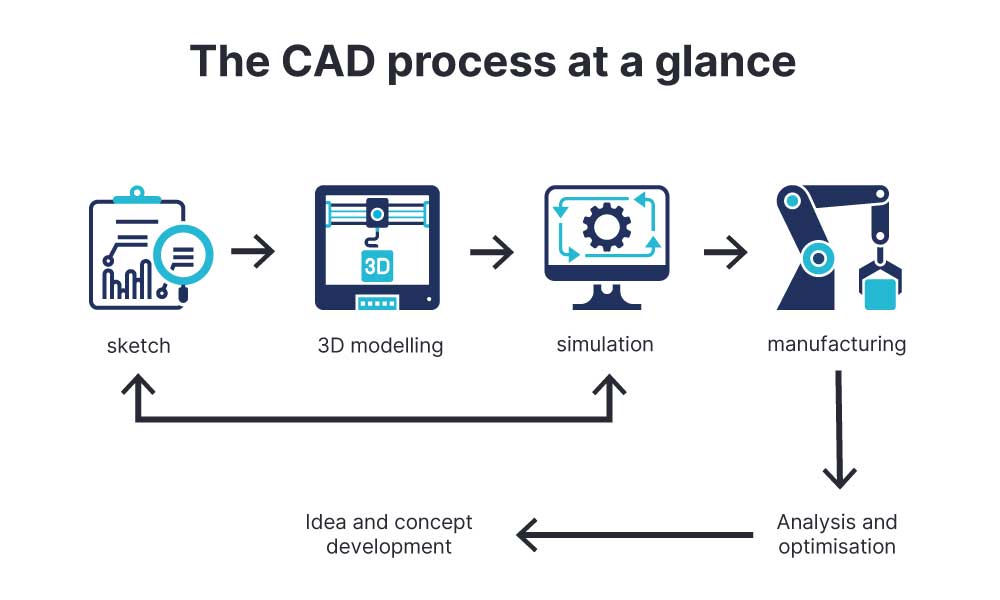
How Does CAD Work in Practice?
CAD software combines various modules that generate, store, and visualise geometric data. The core principle remains the same: every design is created as a digital 3D model containing all relevant information – from geometries and materials to tolerances.
Structure and Components of CAD Software
A modern CAD system consists of several core modules that offer a wide range of functions. The geometry kernel (modeler) precisely and reliably calculates 2D and 3D geometries. The user interface allows models to be created and edited intuitively. Data management stores models and metadata and is often linked to PDM (Product Data Management) or PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) systems. Interfaces ensure communication with other applications, such as CAM or FEM.
This structure ensures that CAD operates efficiently as part of the overall process chain. CAD is used not only for design but also for the analysis, documentation, and presentation of technical solutions.
From Concept to 3D Model
A typical CAD process begins with a sketch that serves as the foundation. Technical drawings, solid bodies, or surface models are then created to define the product’s shape. Through parametric modelling, dimensions and dependencies can be specified so that any changes automatically adjust across the design.
Modern CAD programmes are available for almost every requirement. They enable the combination of individual components into complete assemblies. Designers check for collisions, movements, and clearances to ensure that all parts fit together correctly.
The choice of CAD software depends heavily on the specific requirements of a project. It must combine technical accuracy, user-friendliness, and compatibility with other systems.
The result is a CAD model that serves as a complete digital representation of the product – forming the basis for simulation, manufacturing, and presentation.
Discover our ergoCAM software solution – for outstanding cutting results and maximum performance from your cutting machines!
Key CAD Programmes at a Glance
The market for CAD solutions is diverse. There are numerous CAD programmes that differ in functionality, specialisation, and pricing models. Choosing the right CAD software strongly depends on the specific requirements of the company and the industry.
Some tools are particularly suited to mechanical engineering, while others are designed for architecture, product design, or research. Each programme offers a wide range of features for designing, simulating, and analysing models. This diversity allows companies to tailor systems precisely to their processes.

Differences in Application and Industry
- AutoCAD (Autodesk) is a classic choice for 2D and simple 3D designs. It is widely used in architecture and construction.
- SolidWorks (Dassault Systèmes) is popular in mechanical engineering and known for its intuitive operation and flexible modelling capabilities.
- Fusion 360 (Autodesk) integrates CAD, CAM, and simulation in a single platform. It primarily targets smaller companies that prefer agile workflows.
- CATIA (Dassault Systèmes) is considered a premium solution for complex assemblies and high-precision developments, particularly in the aerospace industry.
Each of these solutions has its advantages and disadvantages. While cloud-based systems promote collaboration and scalability, locally installed systems offer higher data security and system stability.
Licensing Models and Cloud Solutions
In the past, companies purchased their software permanently. Today, providers increasingly rely on subscription models. These offer flexibility but involve ongoing costs. CAD is now frequently used in cloud environments to connect teams across different locations.
Cloud solutions simplify collaborative work and ensure transparent workflows. They promote innovation by allowing multiple developers to work on projects simultaneously. At the same time, companies must pay close attention to data protection, licence management, and internet availability.
Typical Areas of Application
Today, CAD serves as a key technology across nearly all industrial sectors. It supports the entire product lifecycle – from the initial idea to series production. The use of software in development enables processes to be digitalised, risks to be reduced, and development times to be shortened.
Industry and Mechanical Engineering
In mechanical engineering, CAD supports engineers in designing complex systems and tools. The systems take into account the specific requirements of each project, such as material properties, tolerances, and manufacturing techniques. Integration with CAM creates continuous process chains that enhance efficiency and precision.
CAD also provides significant advantages for communication between design, production, and quality assurance. Teams work on the same data set, ensuring full transparency of changes and versions at all times.
Architecture and Construction
In architecture, CAD enables precise planning of buildings, infrastructure, and interior spaces. CAD programmes in this field vary – from specialised BIM solutions to universal 3D modelling tools. Architects use these tools to simulate designs, compare variants, and make construction processes more efficient.
The technology facilitates collaboration between architects, engineers, and construction companies. Through digital model exchange, realistic project visualisations are created, allowing potential errors to be identified early.
Product Design and Consumer Goods
In product design, CAD is used to develop ergonomic and functional products. Designers visualise shapes, colours, and surfaces, assessing their impact in a realistic context. Modern tools make it possible to create technical drawings and 3D models that accurately represent materials, lighting conditions, and textures.
For designers, CAD offers a wide range of creative possibilities – from concept development and simulation to final presentation. The result is products that are both aesthetically appealing and technically optimised.
Maximise efficiency and precision in your production for sustainable competitiveness and future security.
Advantages and Benefits of CAD
CAD offers significant advantages for companies that aim to make their development processes more efficient. The technology enables precise creation of drawings and models and allows for quick adaptation to new requirements. It increases accuracy, reduces errors, and improves communication between development, production, and quality assurance.
As an indispensable tool in modern product development, CAD supports designers, engineers, and entire teams in realising innovative solutions. The systems integrate functions for simulation, analysis, and documentation, ensuring a seamless digital workflow.
Another major advantage lies in its flexibility: the right CAD software can be tailored to company size, industry, and project type. It provides tools for creating technical drawings, 3D modelling, and data analysis. This flexibility saves time and significantly enhances productivity.
The advantages and disadvantages depend strongly on the system architecture. While cloud solutions enable location-independent collaboration and easy updates, local installations offer greater control over data and processes. Companies therefore choose their systems based on needs, security requirements, and team structure.
Key Advantages at a Glance:
- Higher precision: Minimal tolerances and exact geometries.
- Increased efficiency: Faster workflows through automated functions and templates.
- Optimised collaboration: Shared data platforms allow parallel work.
- Seamless integration: CAD models can be directly transferred into CAE simulations or CAM manufacturing programmes.
- Error reduction: Early detection of conflicts or weak points in the digital model.

Challenges in Using CAD
Despite all its advantages, the use of CAD also comes with certain challenges:
- High acquisition costs: Licences and hardware can require significant investment.
- Training effort: Professional use demands solid technical knowledge and expertise.
- Compatibility issues: Different file formats often make data exchange between systems difficult.
- Data security: Especially in cloud-based solutions, data protection and access control are critical factors.
These aspects illustrate that the successful implementation of CAD is not only a technical task but also an organisational one.
Looking Ahead – Trends and Innovations
The future of CAD is closely linked to artificial intelligence, generative design, and collaborative platforms. The goal is to make design processes even more efficient, sustainable, and automated.

AIArtificial Intelligence – computer systems that can simulate human-like thinking processes and decisions. and Automation in the Design Process
Artificial intelligence is transforming the way companies design and develop products. It analyses existing models, suggests optimisations, and automatically generates new variants. This development improves not only parametric modelling but also direct modelling of complex structures, making design processes more flexible and adaptable.
CAD is often combined with generative design to create new, more efficient forms. This method uses defined parameters such as weight, stability, or material consumption, enabling designs that would have been nearly impossible to realise manually.
Sustainability and Material Efficiency
Forward-looking CAD systems integrate functions for life cycle analysis (LCA) and material optimisation. This allows engineers to evaluate the carbon footprint or energy consumption of a product as early as the design phase.
The focus is increasingly shifting towards sustainable materials, resource-efficient design, and integration into Industry 5.0 concepts.
Conclusion – CAD as a Key Technology
Computer-aided design has evolved from a purely technical design tool into a central pillar of digital product development. It combines creative design with technical precision, enabling companies to implement innovations more quickly and efficiently.
CAD provides seamless digital workflows – from the initial idea through simulation to production. This integration creates transparency, reduces costs, and enhances product quality.
Forward-thinking companies rely on CAD to respond flexibly to market demands. As such, the technology remains a decisive factor for competitiveness and sustainable growth in the industry.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Computer-Aided Design
Which hardware requirements should a workstation meet for modern CAD software?
Powerful processors, sufficient RAM, a professional graphics card and fast SSD storage are important in order to work smoothly even with large assemblies.
How do desktop CAD applications differ from cloud-based CAD solutions?
Desktop programmes offer maximum computing power locally on the device, while cloud CAD enables location-independent collaboration and flexible scaling – ideal for distributed teams.
How can data quality in CAD projects be ensured in the long term?
Standardised naming, clean version management and fixed modelling guidelines help ensure consistent CAD data throughout the entire product life cycle.
What role does CAD play in the digitalisation of supply chains?
Through the exchange of standardised 3D models and manufacturing data, suppliers, manufacturers and partners can collaborate more efficiently and reduce sources of error.
How does CAD support the creation of technical documentation?
Many systems allow the automatic derivation of exploded views, bills of materials or assembly instructions directly from the 3D model – without manual reworking.
Which strategies help standardise CAD workflows within a company?
Approaches such as central templates, defined design rules and regular training improve consistency and reduce errors throughout the entire development process.



