
Predictive Maintenance: Smart Ausfälle stoppen für eine vorausschauende Instandhaltung
8. September 2025
Stellen Sie sich vor, Sie könnten ungeplante Ausfälle und teure Wartungen vermeiden, bevor sie überhaupt auftreten. Predictive Maintenance – die prädiktive Wartung – macht das möglich und revolutioniert die Art, wie Unternehmen ihre Abläufe optimieren und Ressourcen schonen. In einer Welt, in der Produktionsstillstände hohe Kosten verursachen und Effizienz zum Wettbewerbsvorteil wird, bietet Predictive MaintenanceVorausschauende Wartung mit Datenanalyse und KI zur Vorhersage von Maschinenausfällen vor deren Eintreten. einen unschätzbaren Mehrwert.
Sie wollen wissen, wie Sie Predictive Maintenance erfolgreich umsetzen, welche wirtschaftlichen Vorteile entstehen und welche Herausforderungen zu meistern sind? Dieser Beitrag liefert die Antworten und zeigt, wie Predictive Maintenance Ihre Betriebsabläufe transformieren kann und wie Sie mit IoT, Machine Learning und Big Data Anlagenausfälle vermeiden und Kosten senken können.

1. Einführung in Predictive Maintenance
Predictive Maintenance (PdM) ist eine Strategie, die auf der Überwachung des Zustands von Maschinen und Anlagen basiert, um Instandhaltungsarbeiten nur dann durchzuführen, wenn sie tatsächlich erforderlich sind. Diese vorausschauende Methode nutzt fortschrittliche technische Lösungen wie IoT-Sensoren, Machine LearningMaschinelles Lernen – Algorithmen zur selbstständigen Mustererkennung in Produktionsdaten für automatische Prozessoptimierung ohne manuelle Programmierung. und Big DataRiesige Datenmengen, die zu groß und komplex für herkömmliche Datenverarbeitungssoftware sind. Analytics, um den optimalen Zeitpunkt für Wartungsarbeiten voraussagen. Dabei werden kontinuierlich Daten wie Vibrationen, Temperaturen und Druckwerte gesammelt und analysiert, um Muster und Anomalien zu erkennen, die auf bevorstehende Ausfälle hinweisen.
Unterschied zwischen Predictive und Preventive Maintenance
Während Predictive Maintenance auf der Prognose von Ausfällen basiert, setzt Preventive Maintenance auf regelmäßige, zeitgesteuerte Wartung. Preventive Maintenance erfolgt nach festen Intervallen oder Nutzungszyklen, unabhängig vom tatsächlichen Zustand der Maschine, was zu unnötigen Wartungsmaßnahmen und damit verbundenen Kosten führen kann. Im Gegensatz dazu greift Predictive Maintenance gezielt und effizient ein, sobald ein tatsächlicher Bedarf besteht, wodurch die Wartungskosten gesenkt und die Maschinenverfügbarkeit erhöht werden.
Setzen Sie neue Maßstäbe in der Instandhaltung!
Maximieren Sie die Effizienz und Präzision in Ihrer Produktion, für nachhaltige Wettbewerbsfähigkeit und Zukunftssicherheit.
2. Technologische Grundlagen und Innovationen
IoT-Sensortechnologie und Entwicklungen
IoT-Sensoren erfassen kontinuierlich Daten über den Zustand von Maschinen und Anlagen. Diese Sensoren können verschiedene physikalische Parameter wie Vibration, Temperatur und Druck messen. Die Echtzeitdaten ermöglichen eine präzise Überwachung und frühzeitige Erkennung potenzieller Störungen. Die Entwicklung immer kleinerer und leistungsfähigerer Sensoren sowie ihre Integration in bestehende Systeme hat die Verbreitung und Effizienz von Predictive Maintenance erheblich verbessert.
Machine Learning Algorithmen für smart Maintenance
Machine Learning-Algorithmen analysieren die erfassten Daten und erkennen Muster, die auf bevorstehende Ausfälle hinweisen. Diese Algorithmen lernen kontinuierlich aus historischen Daten und aktuellen Messwerten, um immer präzisere Vorhersagen zu ermöglichen. Durch die Anwendung von Techniken wie Anomalieerkennung und prädiktiver Modellierung können Wartungsteams frühzeitig Maßnahmen ergreifen, um ernsthafte Probleme vorzubeugen.
Edge ComputingDatenverarbeitung direkt vor Ort an Maschinen und Sensoren, ohne Umweg über zentrale Server oder Cloud. in der Wartung
Edge Computing ermöglicht die Verarbeitung von Daten direkt an der Quelle, also in der Nähe der Maschinen. Dies reduziert die Latenz und ermöglicht schnellere Reaktionen auf potenzielle Probleme. Durch die dezentrale Datenverarbeitung können große Datenmengen effizient gehandhabt werden, ohne dass sie ständig in zentrale Rechenzentren übertragen werden müssen. Dies ist besonders nützlich in Umgebungen mit begrenzter Konnektivität oder hohen Latenzanforderungen.
Einfluss von 5G auf Predictive Maintenance
Die Einführung von 5G-Technologie ermöglicht eine schnellere und zuverlässigere Datenübertragung. Mit höheren Bandbreiten und geringeren Latenzzeiten verbessert 5G die Kommunikation zwischen IoT-Sensoren und zentralen Datenplattformen erheblich. Dies führt zu einer effizienteren Datenverarbeitung und ermöglicht Echtzeitanalysen, die die Effizienz von Predictive Maintenance-Systemen weiter steigern. 5G unterstützt zudem die Integration und Nutzung von Augmented Reality und anderen technische Fortschritte in Wartungsprozessen.

3. Implementierung und Best Practices
Eine erfolgreiche Einführung von Predictive Maintenance erfordert eine klare Strategie, die technische, organisatorische und menschliche Faktoren gleichermaßen berücksichtigt.
- Bedarfsermittlung: Analysieren Sie, welche Maschinen und Prozesse den größten Einfluss auf Produktivität und Kosten haben. Berücksichtigen Sie Ausfallraten, Wartungsintervalle und bestehende Datenquellen, um das Potenzial für Predictive Maintenance realistisch einzuschätzen.
- Technologieauswahl: Wählen Sie geeignete IoT-Sensoren, Datenplattformen und Analyse-Tools, die kompatibel mit Ihrer bestehenden IT- und Produktionsumgebung sind. Skalierbarkeit und Datensicherheit sollten dabei zentrale Entscheidungskriterien sein.
- Pilotprojekt: Starten Sie mit einem klar abgegrenzten Anwendungsfall, um die Wirksamkeit zu testen und erste Erfahrungen zu sammeln. Ein erfolgreicher Pilot liefert wertvolle Erkenntnisse über Datenqualität, Prozessintegration und Schulungsbedarf.
- Skalierung und Change Management: Überführen Sie bewährte Prozesse schrittweise in den Regelbetrieb. Begleiten Sie die Einführung mit gezielten Schulungen, um Akzeptanz und Kompetenz im Team zu fördern. Ein gutes Change Management ist entscheidend, um Widerstände zu vermeiden und die Vorteile der neuen Technologie vollständig zu realisieren.
Ein fundierter Business Case unterstützt die Argumentation für Investitionen. Neben direkten Kosteneinsparungen durch reduzierte Stillstände sollten auch langfristige Effekte – etwa eine höhere Anlagenverfügbarkeit und verlängerte Lebensdauer – berücksichtigt werden. So lässt sich der Return on Investment (ROI) transparent und nachvollziehbar darstellen.
4. Die Rolle von Big Data und Analytics
Datenerfassung und -analyse
Erfassen Sie kontinuierlich Daten von Ihren Maschinen und Anlagen und nutzen Sie fortschrittliche Analysetools, um diese Daten zu interpretieren und wertvolle Erkenntnisse zu gewinnen. Die genaue Datenerfassung und -analyse sind entscheidend, um präzise Vorhersagen und fundierte Entscheidungen zu treffen. Nutzen Sie sowohl historische als auch Echtzeitdaten, um umfassende Einblicke in den Zustand und die Leistung Ihrer Maschinen zu erhalten.
Integration von Datenquellen
Sorgen Sie dafür, dass alle relevanten Datenquellen in einer zentralen Plattform zusammengeführt werden. Dies ermöglicht eine umfassende Analyse und bessere Vorhersagen. Integrieren Sie Daten aus verschiedenen Systemen wie ERPEnterprise Resource Planning – Software zur integrierten Verwaltung aller Unternehmensprozesse und Ressourcen., CMMS und IoT-Plattformen, um ein vollständiges Bild zu erhalten und datengesteuerte Entscheidungen zu unterstützen.
Lesen Sie dazu auch unseren Beitrag: Was ist das Industrial Internet of Things (IIoTIIoT ist die internetbasierte Vernetzung industrieller Maschinen, Anlagen und Geräte zur Datensammlung und Prozessoptimierung)?
Nutzung von Predictive Analytics für die vorausschauende Wartung
Nutzen Sie Predictive Analytics, um zukünftige Wartungsbedarfe präzise vorherzusagen und so die Effizienz und Verfügbarkeit Ihrer Anlagen zu maximieren. Predictive Analytics kombiniert statistische Modelle, maschinelles Lernen und Datenanalysetechniken, um Muster und Trends zu identifizieren, die auf bevorstehende Wartungsanforderungen hinweisen. Dies ermöglicht proaktive Maßnahmen und verbessert die Planung und Durchführung von Systemwartung.
5. Branchenspezifische Anwendungen
Manufacturing 4.0
Predictive Maintenance ist ein zentraler Bestandteil der Industrie 4.0 und hilft Fertigungsunternehmen, Ausfallzeiten zu minimieren und die Produktivität zu steigern. Durch die Integration von IoT-Sensoren und Datenanalysen können Hersteller den Zustand ihrer Maschinen kontinuierlich überwachen und Wartungsmaßnahmen bedarfsgerecht planen. Dies führt zu einer höheren Effizienz und einer besseren Nutzung der Ressourcen.
Energiesektor und Utilities
Energieversorger können durch Predictive Maintenance die Zuverlässigkeit ihrer Netze erhöhen und Instandsetzungskosten senken. Die kontinuierliche Überwachung von Transformatoren, Generatoren und anderen kritischen Komponenten ermöglicht frühzeitige Eingriffe und verhindert kostspielige Ausfälle. Dies trägt zur Stabilität und Effizienz der Energieversorgung bei.
Healthcare Equipment
Krankenhäuser und andere Gesundheitseinrichtungen nutzen Predictive Maintenance, um die Verfügbarkeit und Sicherheit medizinischer Geräte zu gewährleisten. Durch die Überwachung von Diagnostikgeräten, Beatmungsgeräten und anderen lebenswichtigen Geräten können potenzielle Probleme frühzeitig erkannt und behoben werden, wodurch die Patientensicherheit erhöht und die Betriebskosten gesenkt werden.
Smart Buildings
In intelligenten Gebäuden sorgt Predictive Maintenance für den reibungslosen Betrieb von Heizungs-, Lüftungs- und Klimaanlagen. Sensoren überwachen kontinuierlich den Zustand der HLK-Systeme und melden Anomalien, bevor sie zu größeren Problemen führen. Dies verbessert den Komfort und die Energieeffizienz der Gebäude und reduziert die Servicekosten.
Prozessindustrie
In der Prozessindustrie hilft Predictive Maintenance, die Verfügbarkeit und Effizienz komplexer Anlagen zu maximieren. Durch die Überwachung von Pumpen, Ventilen und anderen kritischen Komponenten können Unternehmen sicherstellen, dass ihre Produktionsanlagen optimal funktionieren und ungeplante Ausfallzeiten minimiert werden.
6. Datensicherheit und Compliance
- Cybersecurity in Predictive Maintenance Systemen: Implementieren Sie robuste Cybersecurity-Maßnahmen zum Schutz Ihrer Daten und Systeme vor unbefugtem Zugriff und Angriffen. Dies umfasst die Verschlüsselung von Daten, den Einsatz von Firewalls und Intrusion-Detection-Systemen sowie regelmäßige Sicherheitsüberprüfungen und Updates. Stellen Sie sicher, dass alle Systeme und Netzwerke den höchsten Sicherheitsstandards entsprechen.
- Datenschutzaspekte: Stellen Sie sicher, dass Ihre Predictive Maintenance-Lösungen allen relevanten Datenschutzbestimmungen entsprechen. Dies umfasst die Einhaltung von Vorschriften wie der EU-Datenschutz-Grundverordnung (DSGVO) und anderen regionalen Datenschutzgesetzen. Implementieren Sie Datenschutzrichtlinien und -verfahren, um die Vertraulichkeit und Integrität der gesammelten Daten zu gewährleisten.
- Industriestandards und Zertifizierungen: Halten Sie sich an Industriestandards und Zertifizierungen, um die Qualität und Sicherheit Ihrer Predictive Maintenance-Systeme zu gewährleisten. Dazu gehören Standards wie ISO 27001 für Informationssicherheitsmanagement und ISO 55001 für Asset Management. Die Einhaltung dieser Standards zeigt das Engagement Ihres Unternehmens für Best Practices und kontinuierliche Optimierung.
- Cloud vs. On-Premise Lösungen: Wägen Sie die Vor- und Nachteile von Cloud-basierten und On-Premise Lösungen ab, um die beste Option für Ihr Unternehmen zu wählen. Cloud-basierte Lösungen bieten Skalierbarkeit, Flexibilität und geringere Anfangskosten, während On-Premise-Lösungen eine größere Kontrolle über Daten und Systeme ermöglichen. Berücksichtigen Sie Ihre spezifischen Anforderungen und Ressourcen, um die optimale Lösung zu finden.
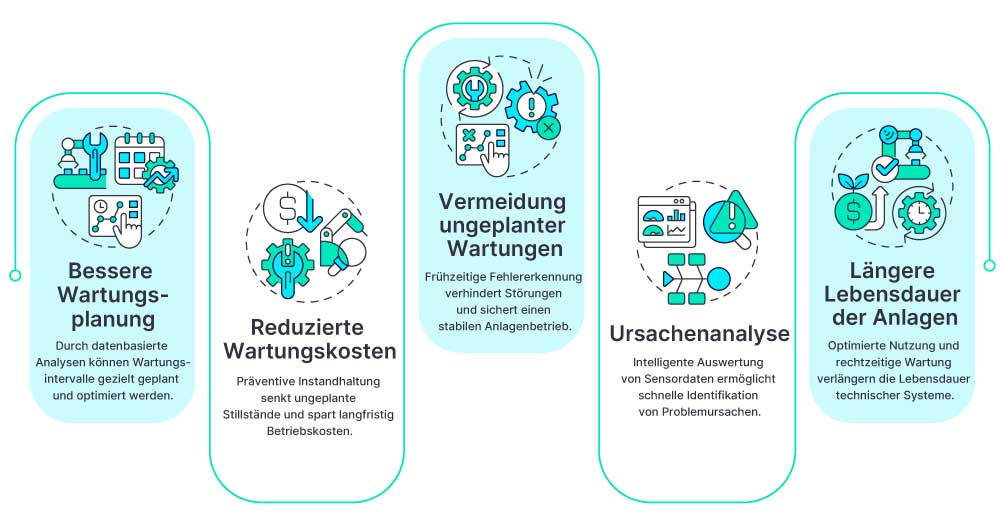
7. Wirtschaftliche Aspekte
Kosteneinsparungspotenziale
Predictive Maintenance hilft, bei der Senkung von Wartungskosten und bei der Vermeidung teurer Ausfallzeiten. Durch die frühzeitige Erkennung und Behebung von Problemen können Unternehmen ungeplante Stillstände minimieren und die Effizienz ihrer Wartungsintervalle verbessern. Dies führt zu erheblichen Kosteneinsparungen und einer höheren Rentabilität.
Verfügbarkeitssteigerung
Durch die frühzeitige Erkennung von Problemen wird die Verfügbarkeit Ihrer Maschinen und Anlagen maximiert. Predictive Maintenance trägt dazu bei, die Betriebszeit zu erhöhen und die Produktionskapazität zu maximieren, indem sie sicherstellt, dass Maschinen und Anlagen in optimalem Zustand bleiben.
Personalressourcenoptimierung
Optimieren Sie den Einsatz Ihrer Wartungsteams und verbessere die Planung von Wartungsarbeiten. Predictive Maintenance ermöglicht eine effizientere Nutzung von Personalressourcen, indem sie Wartungsaufgaben basierend auf tatsächlichem Bedarf und nicht auf starren Zeitplänen plant. Dies führt zu einer besseren Arbeitsauslastung und einer höheren Zufriedenheit der Mitarbeiter.
Versicherungsaspekte
Predictive Maintenance kann zu niedrigeren Versicherungsprämien führen, da das Risiko von Ausfällen und Schäden reduziert wird. Versicherungsunternehmen erkennen die Vorteile von Predictive Maintenance an und bieten oft günstigere Tarife für Unternehmen, die diese Technologien einsetzen.
Total Cost of Ownership
Reduzieren Sie die Gesamtkosten des Betriebs deiner Maschinen und Anlagen durch effizientere Wartung und längere Lebensdauer. Predictive Maintenance trägt dazu bei, die Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) zu senken, indem sie ungeplante Ausfallzeiten minimiert, die Lebensdauer von Maschinen verlängert und die Effizienz der Wartungsprozesse erhöht.
Lesen Sie auch unsere: Clouver Broschüre – Ihre IIoT-Lösung für mehr Transparenz und Effizienz in der Produktion
8. Integration und Schnittstellen
Predictive Maintenance entfaltet sein volles Potenzial erst durch die nahtlose Integration in bestehende Systeme.
ERP-Systeme verknüpfen Wartungsinformationen mit Produktions- und Betriebsdaten und schaffen so eine zentrale Grundlage für Planung, Analyse und Steuerung.
Über CMMS-Systeme (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems) lassen sich Wartungsaufträge automatisch generieren, dokumentieren und nachverfolgen – für maximale Transparenz und Effizienz.
IoT-Plattformen erfassen kontinuierlich Sensordaten und ermöglichen in Kombination mit Cloud-Services eine skalierbare Datenspeicherung und Echtzeitanalyse großer Datenmengen.
Mobile Lösungen stellen sicher, dass Techniker jederzeit auf aktuelle Informationen zugreifen und Wartungsaufgaben direkt vor Ort effizient umsetzen können.
Eine durchdachte Systemintegration sorgt somit für einen reibungslosen Informationsfluss – von der Maschine bis zur Managementebene – und bildet die Basis für eine vernetzte, datengetriebene Instandhaltungsstrategie.
9. Zukunftstrends und Entwicklungen
- KI-gestützte Predictive Maintenance: Künstliche Intelligenz (KI) wird die Genauigkeit und Effizienz von Predictive Maintenance weiter verbessern. Durch den Einsatz von fortschrittlichen Algorithmen und maschinellem Lernen können KI-Systeme komplexe Muster und Zusammenhänge in großen Datenmengen erkennen, die für menschliche Analysten schwer zu erfassen sind. Dies ermöglicht präzisere Vorhersagen und proaktivere Wartungsstrategien.
- Autonomous Maintenance: Autonome Wartungssysteme könnten in Zukunft Wartungsarbeiten ohne menschliches Eingreifen durchführen. Durch den Einsatz von Robotik und KIKünstliche Intelligenz – Computersysteme, die menschenähnliche Denkprozesse und Entscheidungen simulieren können. können solche Systeme selbstständig Inspektionen, Diagnosen und Reparaturen durchführen, was die Effizienz und Genauigkeit der Wartungsprozesse weiter erhöht.
- Sustainable Maintenance: Nachhaltige Wartungspraktiken zielen darauf ab, den ökologischen Fußabdruck von Wartungsarbeiten zu minimieren. Durch den Einsatz von Predictive Maintenance können Unternehmen den Energieverbrauch und die Abfallproduktion reduzieren, indem sie nur dann Wartungsarbeiten durchführen, wenn sie tatsächlich erforderlich sind. Dies trägt zur Schonung der Umwelt und zur Erreichung von Nachhaltigkeitszielen bei.
Fazit & Handlungsempfehlung
Predictive Maintenance ist mehr als nur ein Trend – sie markiert einen Wendepunkt in der Wartungstechnologie. Durch den Einsatz von IoT-Sensoren, Machine Learning und Big Data Analytics ermöglicht sie präzise Vorhersagen von Wartungsbedarfen und reduziert Ausfallzeiten sowie Kosten. Unternehmen steigern so ihre Effizienz, verlängern die Lebensdauer ihrer Maschinen und schonen Ressourcen.
Die Technologie ist vielseitig einsetzbar – von der Fertigung über den Energiesektor bis hin zu Smart Buildings und dem Gesundheitswesen. Predictive Maintenance senkt nicht nur Betriebskosten, sondern fördert auch Nachhaltigkeit, indem unnötige Reparaturen und Energieverschwendung vermieden werden.



